Leading Coefficient of a Polynomial Function


What is The Leading Coefficient of a Polynomial Function?
Definition
The leading coefficient of a polynomial function is the coefficient of the term with the highest degree when the polynomial is expressed in standard form. The standard form of a polynomial arranges the terms in descending order of their degree, which means you start with the term that has the largest exponent and proceed to the term with the smallest exponent.
Key Points:
Degree of a Polynomial: The degree of a polynomial is the highest power of the variable in the polynomial. For example, in $3x^4 - 5x^3 + 2x^2 - x + 7$, the degree is 4 because the highest power of $x$ is 4.
Leading Term: The leading term in a polynomial is the term with the highest degree. Using the example above, $3x^4$ is the leading term.
Leading Coefficient: The leading coefficient is the coefficient of the leading term. In $3x^4 - 5x^3 + 2x^2 - x + 7$, the leading coefficient is 3.
Importance of the Leading Coefficient:
Determines End Behavior: The leading coefficient, along with the degree of the polynomial, significantly influences the graph's end behavior (how the graph behaves as $x$ approaches infinity or negative infinity).
Influence on Graph Shape: For even-degree polynomials, a positive leading coefficient implies the graph opens upwards (like a parabola opening upwards), and a negative leading coefficient implies it opens downwards. For odd-degree polynomials, a positive leading coefficient results in the graph rising to the right and falling to the left, while a negative leading coefficient reverses this behavior.
Polynomial Forms and Leading Coefficients:
- Polynomials can be presented in various forms, but the standard form is most conducive for quickly identifying the leading coefficient.
- For polynomials not in standard form (e.g., factored form or not sorted by degree), rearranging or expanding terms may be necessary to find the leading coefficient.
How to Determine the leading coefficients of the polynomial function.
Here's a step-by-step guide to find the leading coefficient:
Step 1: Write the Polynomial in Standard Form
Ensure the polynomial is in standard form, meaning the terms are written in descending order of their degrees (powers of $x$). If the polynomial is not in this form, reorder the terms as necessary.
Step 2: Identify the Leading Term
The leading term is the first term in the polynomial when it's written in standard form, as this term will have the highest degree.
Step 3: Find the Leading Coefficient
The leading coefficient is the numerical coefficient of the leading term identified in Step 2.
Solved Examples of Determining the Leading Coefficient
Example 1: Simple Polynomial
Given $f(x) = 2x^3 - 5x^2 + 3x - 7$,
- The polynomial is already in standard form.
- The leading term is $2x^3$.
- The leading coefficient is 2.
Graph
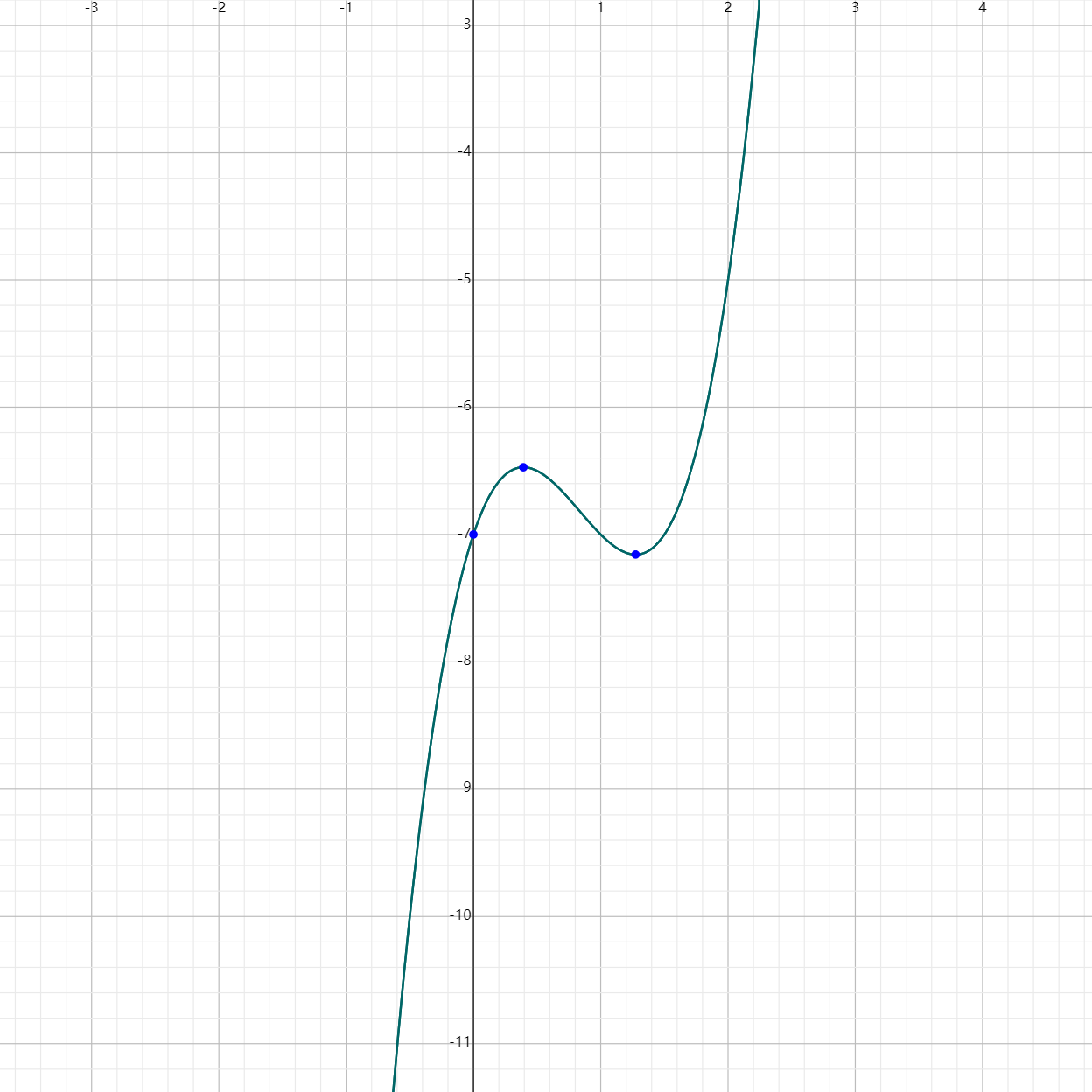
Example 2: Polynomial Not in Standard Form
Given $g(x) = x - 4x^3 + x^5 - 6$,
- First, write it in standard form: $g(x) = x^5 - 4x^3 + x - 6$.
- The leading term is $x^5$.
- The leading coefficient is 1.
Graph
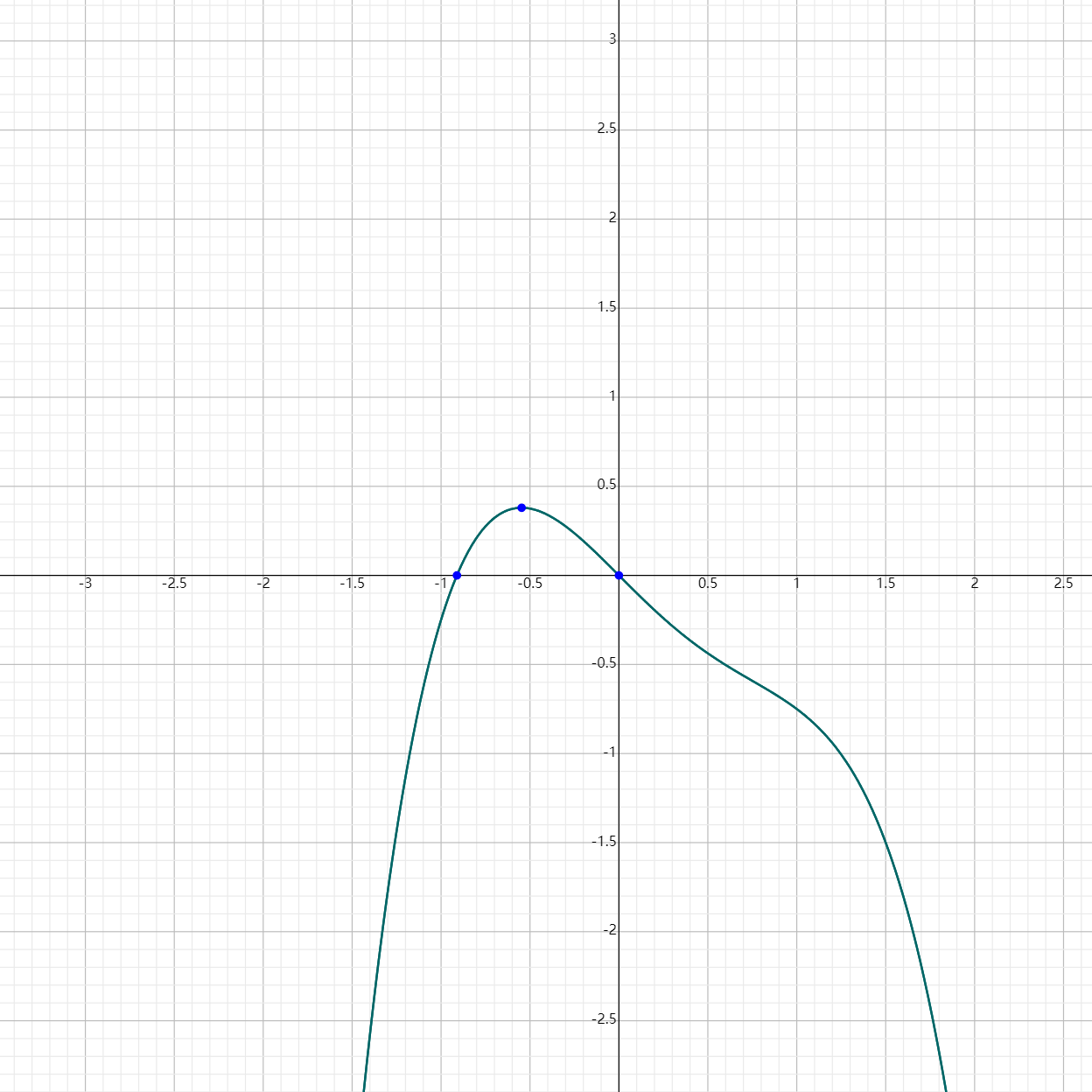
Example 3: Polynomial with Fractional Coefficients
Given $h(x) = -\frac{1}{2}x^4 + \frac{3}{4}x^3 - x$,
- The polynomial is in standard form.
- The leading term is $-\frac{1}{2}x^4$.
- The leading coefficient is $-\frac{1}{2}$.
Graph
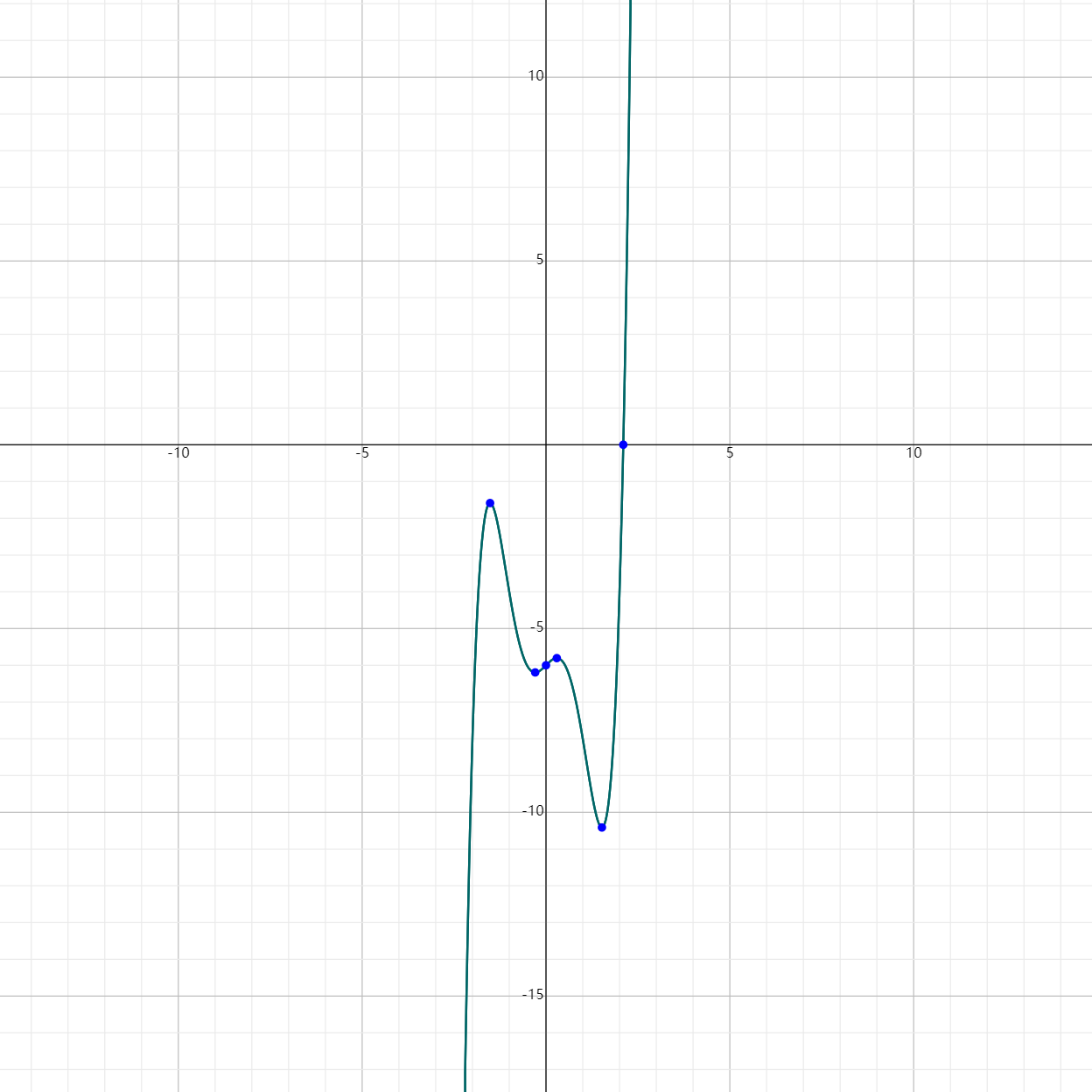
Example 4: Factored Polynomial
Given $k(x) = 2(x - 1)(x^2 + 2x + 3)$,
First, write it in standard form: $k(x) = 2(x - 1)(x^2 + 2x + 3)$.
$k(x) = 2(x - 1)(x^2 + 2x + 3)$
$= (2x - 2)(x^2 + 2x + 3)$.
$= 2x(x^2 + 2x + 3) - 2(x^2 + 2x + 3)$.
$= 2x^3 + 4x^2 + 6x - 2x^2 - 4x - 6$
$= 2x^3 + 2x^2 + 2x - 6$
The leading term is $2x^3$.
The leading coefficient is 2.
Graph
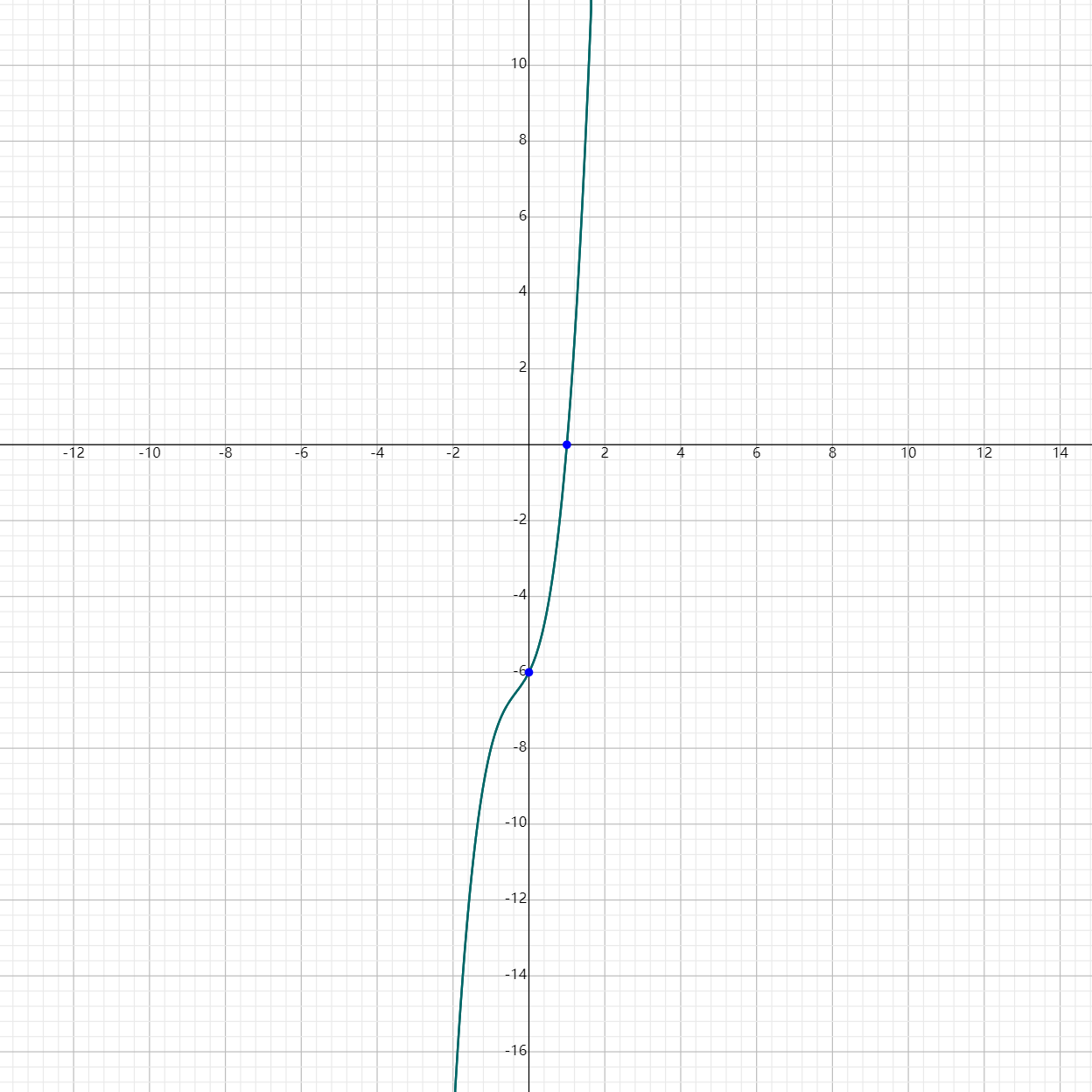
FAQs About The Leading Coefficient
Q: How does the leading coefficient affect the polynomial?
A: The leading coefficient of a polynomial plays a crucial role in determining the overall behavior and characteristics of the polynomial function. Here are some ways in which the leading coefficient affects the polynomial:
End Behavior: The leading coefficient determines the direction in which the polynomial function heads as the independent variable ($x$) approaches positive or negative infinity. Specifically:
- If the leading coefficient is positive, the polynomial function will increase without bound as $x$ goes to both positive and negative infinity. The graph will rise on the right side and rise on the left side.
- If the leading coefficient is negative, the polynomial function will decrease without bound as $x$ goes to both positive and negative infinity. The graph will fall on the right side and fall on the left side.
Number of Turns: The leading coefficient affects the number of turns or bends in the graph of the polynomial. A positive leading coefficient typically leads to an "upward" graph with upward turns, while a negative leading coefficient results in a "downward" graph with downward turns.
Multiplicity of Roots: The leading coefficient influences the multiplicity of roots (zeros) of the polynomial function. Roots with odd multiplicities pierce the x-axis, while roots with even multiplicities touch or bounce off the x-axis. The leading coefficient determines whether these roots are reflected above or below the x-axis.
Growth Rate: The leading coefficient also influences the rate of growth or decay of the polynomial function. A higher absolute value of the leading coefficient typically indicates faster growth or decay of the function.
Relation to Other Coefficients: The leading coefficient interacts with the coefficients of other terms in the polynomial when performing operations such as addition, subtraction, or multiplication of polynomials. It determines the overall magnitude and shape of the polynomial function.
Q: How do you tell if the leading coefficient of a polynomial is positive or negative? A: Determining whether the leading coefficient of a polynomial is positive or negative involves looking at the coefficient of the term with the highest degree in the polynomial expression. Here are the steps to tell if the leading coefficient of a polynomial is positive or negative:
- Identify the Term with the Highest Degree: In a polynomial expression, the term with the highest power of the variable (usually denoted by $x$) is known as the leading term, and the coefficient of this term is the leading coefficient.
- Check the Sign of the Leading Coefficient:
- If the coefficient of the leading term is positive, then the leading coefficient of the polynomial is positive.
- If the coefficient of the leading term is negative, then the leading coefficient of the polynomial is negative.
- Examples:
- In the polynomial $f(x) = 3x^4 - 2x^3 + 5x^2 + 6x + 1$, the leading term is $3x^4$, and the coefficient is $3$, which is positive. Therefore, the leading coefficient is positive.
- In the polynomial $g(x) = -2x^3 + 4x^2 - x + 7$, the leading term is $-2x^3$, and the coefficient is $-2$, which is negative. Therefore, the leading coefficient is negative.
Q: Which is the leading coefficient and constant term in a polynomial function?
A: In a polynomial function, the leading coefficient and the constant term are two key components that give insight into the function's characteristics and behavior.
Leading Coefficient
The leading coefficient is the coefficient of the term with the highest degree (the term with the largest exponent) when the polynomial is expressed in standard form (terms written in descending order of their degrees). This coefficient influences the end behavior of the polynomial's graph and its steepness or spread.
- How to Identify: Look for the term with the highest power of the variable in the polynomial. The numerical factor in front of this term is the leading coefficient.
- Example: In the polynomial $f(x) = 4x^3 - 5x^2 + 2x - 1$, the leading term is $4x^3$, so the leading coefficient is $4$.
Constant Term
The constant term in a polynomial function is the term that does not contain any variables. It's the standalone number within the polynomial expression.
- How to Identify: Look for the term in the polynomial that is not multiplied by any variable. This term remains constant regardless of the value of the variable.
- Example: In the same polynomial $f(x) = 4x^3 - 5x^2 + 2x - 1$, the constant term is $-1$.
Importance
Leading Coefficient:
- It determines the end behavior of the polynomial's graph. For instance, if the leading coefficient is positive and the degree of the polynomial is even, the ends of the graph will point upwards.
- It can affect the curvature and orientation of the polynomial's graph.
Constant Term:
- It affects the polynomial's value when the variable(s) equal zero.
- It can influence the position of the polynomial's graph on the coordinate plane, especially its intersection with the y-axis (the y-intercept).